“My throat has been killing me for four days, but I don’t have a fever,” my patient explained. “Does that mean it’s not serious?”
Sore throats without fever puzzle many people who associate throat infections with elevated temperatures. While fever often accompanies bacterial infections, its absence doesn’t rule out conditions requiring medical attention.
Common Causes Without Fever
Viral infections frequently cause severe throat pain without significant temperature elevation, especially in adults.
Allergic reactions to environmental triggers can create throat irritation and pain that mimics infection.
Acid reflux causes burning throat pain that worsens at night or when lying down, typically without fever.
Dry air exposure from heating systems or mouth breathing creates throat irritation that can be quite painful.
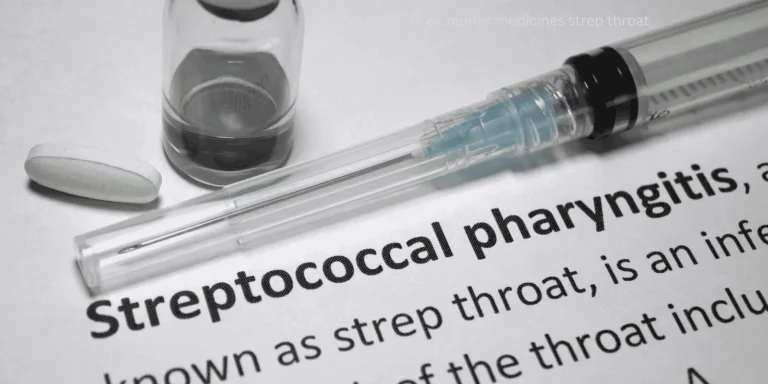
Strep Throat Can Occur Without Fever
Adult strep infections often present with severe throat pain but minimal or no fever, unlike typical childhood presentations.
Early stages of bacterial throat infections may not yet trigger significant fever responses.
Immune system variations mean some people don’t mount strong fever responses to bacterial infections.
Warning Signs That Matter More Than Fever
Severe pain that interferes with swallowing liquids suggests significant throat inflammation requiring evaluation.
Difficulty opening the mouth or neck stiffness indicates possible deeper throat infection or abscess formation.
Drooling or inability to swallow saliva suggests airway swelling that could become dangerous.
Voice changes like muffled speech or “hot potato” voice may indicate throat swelling affecting vocal cords.
Duration Becomes Important
Sudden onset of severe throat pain, even without fever, warrants evaluation for possible strep throat.
Persistent pain lasting more than a week without improvement suggests bacterial infection or other conditions needing treatment.
Progressive worsening over several days indicates possible complications developing.
Associated Symptoms to Monitor
Swollen neck lymph nodes often accompany bacterial throat infections, even when fever is absent.
White patches or pus on throat tissues suggest bacterial infection requiring antibiotic treatment.
Rash development might indicate scarlet fever or other complications of untreated strep throat.
Ear pain along with throat pain suggests possible spread of infection to adjacent structures.
Age-Related Considerations
Adults more commonly experience afebrile (without fever) strep throat compared to children who typically develop high fevers.
Elderly individuals may have blunted fever responses to serious infections, making other symptoms more important.
Immunocompromised people might not mount typical fever responses despite significant bacterial infections.
Testing Remains Important
Rapid strep tests can identify bacterial infections even when fever is absent.
Throat cultures provide definitive diagnosis when rapid tests are negative but clinical suspicion remains high.
Clinical examination helps identify physical signs of bacterial infection beyond just temperature measurement.
Conditions That Mimic Throat Infections
Mononucleosis often causes severe throat pain with minimal fever, especially in teenagers and young adults.
Thyroiditis can create throat pain and swelling that feels like infection but requires different treatment.
Throat cancer occasionally presents as persistent sore throat, particularly in older adults or smokers.
Medication side effects from certain drugs can cause throat dryness and pain without infection.
When Immediate Care Is Needed
Breathing difficulties or feeling that your throat is closing require emergency evaluation.
High-pitched breathing sounds suggest airway narrowing that could become life-threatening.
Severe difficulty swallowing that prevents adequate fluid intake can lead to dehydration.
One-sided throat pain with ear pain may indicate peritonsillar abscess formation.
Home Care Limitations
Pain severity that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter pain relievers suggests need for prescription treatment.
Worsening symptoms despite home remedies like warm salt water gargles and throat lozenges.
Inability to eat or drink adequately due to throat pain requires medical intervention.
Treatment Considerations
Bacterial infections require antibiotic treatment regardless of fever presence to prevent complications.
Viral infections need supportive care but may benefit from prescription pain management for severe cases.
Underlying conditions like acid reflux require specific treatments targeting the root cause.
Prevention and Management
Identify triggers like allergens or reflux that might be causing recurrent throat pain without infection.
Maintain hydration and use humidifiers during dry weather to prevent throat irritation.
Avoid irritants like cigarette smoke and strong chemicals that can inflame throat tissues.
The absence of fever doesn’t mean a sore throat is harmless. Severe, persistent, or worsening throat pain warrants medical evaluation to identify treatable causes and prevent complications.